Geological Survey of Finland organized a two-day short course on geoscientific data analysis and predictive mapping for geoscience students of the Turku and Helsinki Universities. The course was co-funded by the DroneSOM (EIT Raw Materials) and AIMEX (Business Finland) projects.
Course format
Based on the positive feedback about the corresponding course organized last year, the format of the course was held approximately the same, consisting of one full day and two half days of teaching for all the students and a homework exercise to be completed independently after the course. On-line teaching option was utilized for one half day of lectures, while the rest of the teaching was done on site separately in Turku and in Helsinki. There were a total of 12 participants on the course.

Schedule and topics
The lectures consisted of theory of selected predictive modeling methods (logistic regression, random forests, multi layer perceptron, weights of evidence, fuzzy logic) and self-organizing maps. Exercises were done using the EIS toolkit for QGIS and the GisSOM desktop application.
Lectures and exercises 3.-6.11.2025
Day 1, 9-17:
- Predictive modelling methods (Turku students on-site and Helsinki students on-line)
- QGIS/EIS Plugin hands-on exercises (only Turku students, on-site)
Day 2, 9:30-13:30:
- QGIS/EIS Plugin hands-on exercises (only Helsinki students, on-site)
Day 3, 9-17:
- SOM lecture (Helsinki students on-site and Turku students on-line)
- GisSOM hands-on exercises (only Helsinki students, on-site)
Day 4, 9:30-13:30:
- GisSOM hands-on exercises (only Turku students, on-site)
To support the homework, discussion sessions were arranged on 12. and 19.11.2025.
Software
GISSOM
GisSOM is a desktop application for applying self-organizing maps and k-means clustering for a multivariate dataset. Emphasis of the software development has been in the visualization of the results. If the data is spatially referenced, results can be visualized in the spatial frame in addition to the SOM space. Labelled data points can be used to visualize the distribution of known properties/classes in the feature space.
An introduction for GisSOM can be found here.
EIS QGIS PLUGIN
EIS QGIS Plugin is a QGIS based tool for predictive mapping of mineral deposits especially. However, it can be used for any predictive mapping problem where we have several features known across our study area and wish to predict some unknown feature. EIS tools include 1) supervised tools, that require our unknown feature to be known at specified locations and 2) unsupervised tools that use expert knowledge to relate the known features to unknown feature.
EIS Plugin can be added to QGIS from the QGIS Plugin Manager. The required Python library EIS toolkit must be installed from GitHub.
Case studies
The exercises and demonstrations used three case studies:
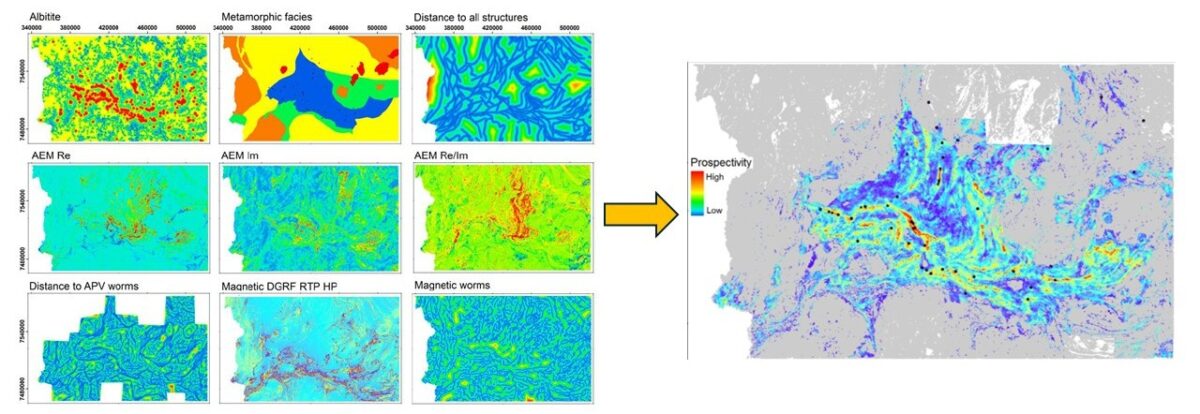
1) Mineral prospectivity modelling of the Central Lapland Greenstone Belt, Finland
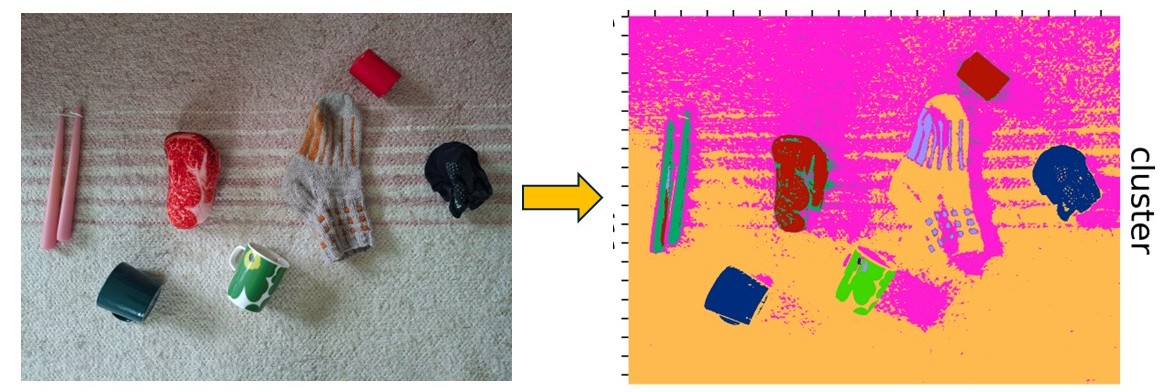
2) Distinguishing objects from a photograph
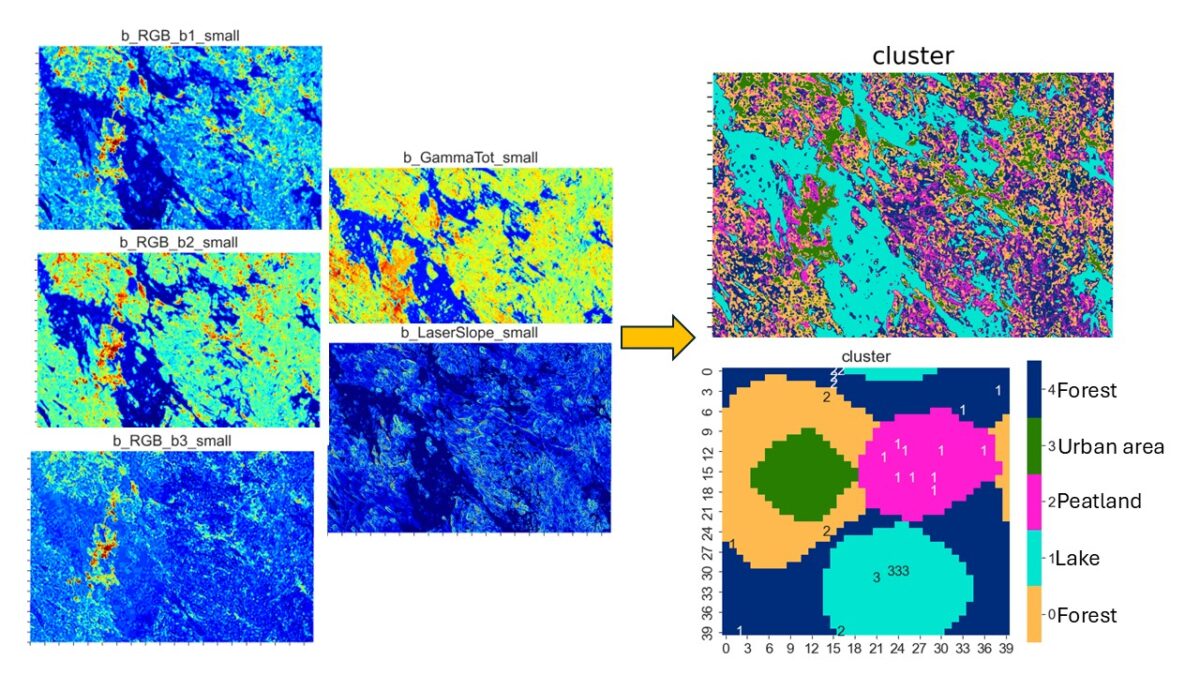
3) Land use mapping of Kuopio surroundings, Finland

Lecturer
Johanna Pesonen, PhD, Senior Researcher in the Geological Survey of Finland, has educational and research background in physics and astronomy and 15 years of experience in geoscientific research. During 2000-2019, she has wokad in both astronomical and geoscience research projects in research institutes and business sector. Since 2019, she has been working at the Geological Survey of Finland as an expert in data analysis and multivariate data integration of different types of geoscientific data. Her aim is to develop new methods for data analysis and to make these methods available to the geoscience research community in form of easy-to-use software tools.